UK online safety bill raises censorship concerns and questions on future of encryption
The U.K. government emphasized press freedom this month when it published the draft online safety bill for social media companies, pledging that the bill would protect both “citizen journalism” and “recognized news publishers” from censorship. Vocal segments of the media not only welcomed the legislation, but actively campaigned for it. When Oliver Dowden, secretary of…

Digital Safety: Internet shutdowns
Internet shutdowns have serious consequences for press freedom and leave journalists struggling to do their job effectively, CPJ has found. Turning off or limiting access to the internet means that media workers are unable to contact sources, fact check data, or file stories until after an event has happened. Shutdowns are more likely to happen…

New York Times journalist Nicole Perlroth on the secret trade in tools used to hack the press
The last time New York Times cybersecurity journalist Nicole Perlroth spoke with Emirati activist Ahmed Mansoor in 2016, his passport had been taken and he had recently been beaten almost to the point of death. “We learned later on that our phone conversation had been tapped, that someone was in his baby monitor, that his…
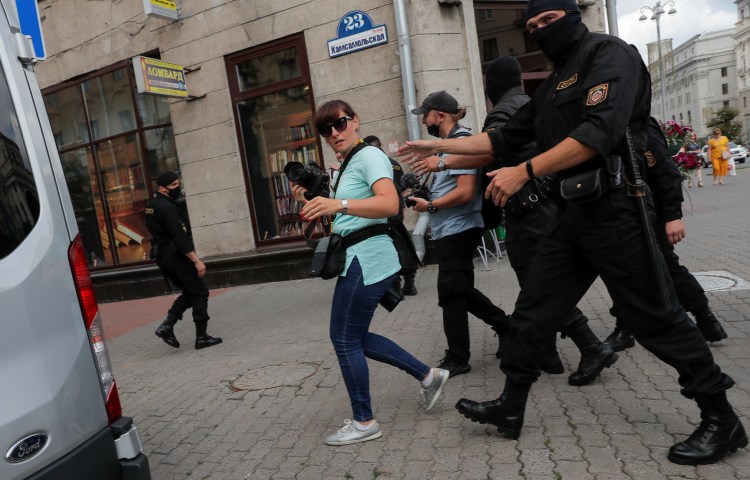

Physical and Digital Safety: Arrest and detention
Covering certain stories–such as human rights abuses, corruption, or civil unrest–can place you at a higher risk of arrest and detention, particularly in countries with authoritarian regimes or with a heavy militarized and police presence. When confronted by the authorities it is generally prudent to comply with their commands, even if they are not lawful,…

Editors’ Checklist: Preparing for U.S. protest assignments
Updated June 8, 2020 The following checklist enables commissioners and editors to understand how well prepared journalists and other media workers are as they cover U.S. protests over police violence. For additional safety information, please see CPJ’s Safety Advisory for covering U.S. protests over police violence. Select your staff after considering: As part of your…

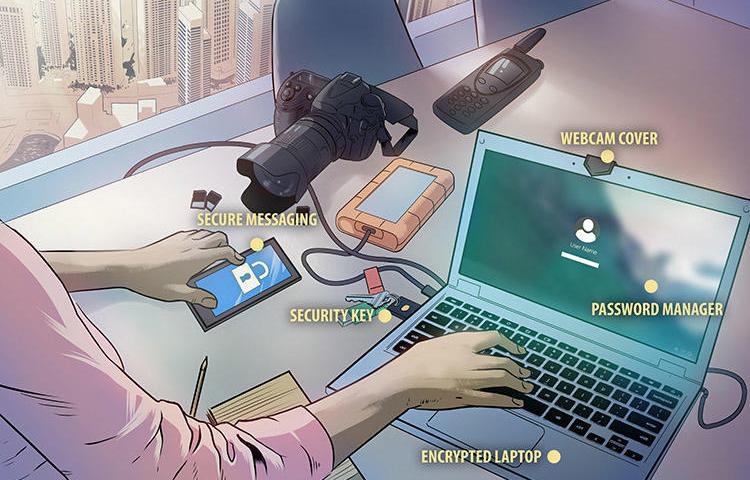
Digital Safety: Protecting against targeted online attacks
Journalists reporting on misinformation, conspiracy theories, and/or false news are frequently left vulnerable to online attacks by those who originate or support these views, as well as by people with strong political leanings. People supporting the spread of this type of information online may organize coordinated attacks with the aim of forcing journalists offline and…

Digital Safety: Working from home
The current global health situation has seen changes to the way journalists do their job, with an increasing number working from home instead of an office. This is creating digital security issues for journalists and media outlets who still need to work during the coronavirus outbreak.

CPJ Safety Advisory: Journalist targets of Pegasus spyware
Pegasus is a spyware created for mobile devices which transforms a cellphone into a mobile surveillance station. Researchers have documented it being used to spy on journalists. This raises significant implications for journalists’ own security and that of their sources.