Dakar, February 5, 2024—Senegalese authorities must restore mobile internet access in the country and the broadcasting license of Walf TV, investigate and hold accountable those responsible for briefly detaining or harassing at least four journalists, and allow the press to report freely, the Committee to Protect Journalists said on Monday.
On Saturday, Senegalese President Macky Sall announced that the presidential election originally scheduled for February 25 would be indefinitely postponed, citing a dispute over the candidate list.
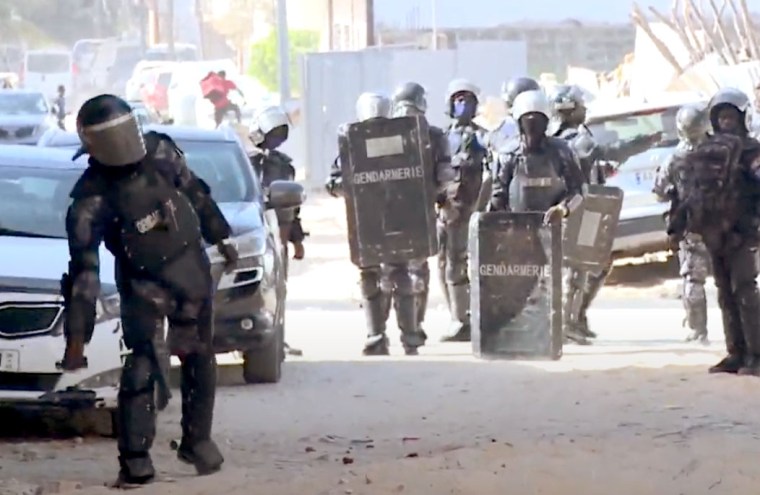
On Monday, police responded to protests with arrests and tear gas, as lawmakers debated the postponement. Late on Monday, parliament voted to reschedule the election to December 15, after security forces removed opposition lawmakers from the chamber.
“Senegalese authorities must immediately lift the mobile internet suspension, reverse the decision to permanently withdraw Walf TV’s broadcasting license, and ensure journalists are not restricted or harassed while covering ongoing protests,” said Angela Quintal, head of CPJ’s Africa program. “As Senegal grapples with the postponement of elections, journalists play a vital role in helping the public understand what is happening. Their ability to report, including via mobile internet, must be protected, not censored.”
On Sunday, Senegal’s Ministry of Communication, Telecommunications, and Digital Economy (MCTPEN) announced it had “temporarily” suspended access to mobile internet due to “hateful and subversive” messages on social media, without indicating the duration of the cutoff.
Internet users began to notice disruption to their mobile connectivity on Monday, according to CPJ’s review of service in the country. Mobile internet accounts for 97% of user connections, according to a September 2023 report by Senegal’s Telecommunications and Postal Regulatory Authority, which regulates the sector.
Also on Sunday, Senegalese authorities permanently withdrew the broadcasting license of Walf TV, the television broadcast service of the privately owned media group Wal Fadjri and one of the country’s major broadcasters, according to CPJ’s review of access to the channel in the country and a copy of the MCTPEN’s decision. The ministry cited Wal Fadjri’s “state of recidivism,” the broadcasting of violent images exposing teenagers, and “subversive, hateful, and dangerous language that undermines state security.”
Walf TV’s broadcasts on Sunday focused on the escalating protests, according to CPJ’s review, which did not identify any calls to violence in that coverage.
The same day, officers with Senegal’s gendarmerie in Dakar, the capital, harassed and briefly detained reporters Sokhna Ndack Mbacké, with the privately owned online news site Agora TV, and Khadija Ndate Diouf, with the privately owned television channel Itv, before releasing them without charge, Mbacké and Diouf told CPJ. Mbacké told CPJ that the officers snatched her phone, insulted both of them, and that one officer threatened her with imprisonment if he saw her again.
Separately, a different group of gendarmerie officers harassed Hadiya Talla, editor-in-chief of the privately owned news site La Vallée Info, interrupting his live broadcast from the protests in Dakar, according to Talla, who spoke to CPJ. First, an officer grabbed Talla’s phone and insulted him before returning it, and then later an officer interrupted his live coverage and ordered him to stop reporting, before letting Talla continue.
The same day, a group of gendarmes twice threw tear gas in the direction of Clément Bonnerot, correspondent for the French-language global broadcaster TV5 Monde, as he stood alone in a Dakar street, filming the security forces, according to Bonnerot and CPJ’s review of a video he shared of the scene. Bonnerot told CPJ that another gendarme later accused him of “following him” and warned not to “provoke him.”

CPJ’s calls to Ibrahima Ndiaye, spokesperson for the gendarmerie, went unanswered.
Also in June 2023, Senegalese authorities in June 2023 suspended Walf TV for a month over its coverage of demonstrations following Sonko’s arrest and threatened to withdraw its broadcasting license in the event of a repeat offense.
Previously, in June, July, and August 2023, the Senegalese government disrupted access to the internet and social media platforms amid protests over the arrest and prosecution of opposition leader Ousmane Sonko. TikTok has remained blocked in the country. Similar blocks of social media platforms were reported in 2021.
Around the world, CPJ has repeatedly documented how internet shutdowns threaten press freedom and journalists’ safety. CPJ offers guidance for journalists on how to prepare for and respond to internet shutdowns.
At least five journalists—Daouda Sow, Maniane Sène Lô, Ndèye Astou Bâ, Papa El Hadji Omar Yally, and Ndèye Maty Niang, who is also known as Maty Sarr Niang—have remained jailed in Senegal since last year in connection with their work.
Editor’s note: This text has been updated in the third paragraph to include the vote to reschedule the election to December 15.
